Phishing Explained
Published Oct 06, 2025 - 👁️ 52 views

Introduction
Phishing is one of the oldest tricks in the hacker’s playbook, yet in 2025 it has evolved into a highly sophisticated, AI‑powered threat. Cybercriminals now use machine learning to craft convincing emails, fake websites, and even voice calls that trick users into revealing sensitive information.
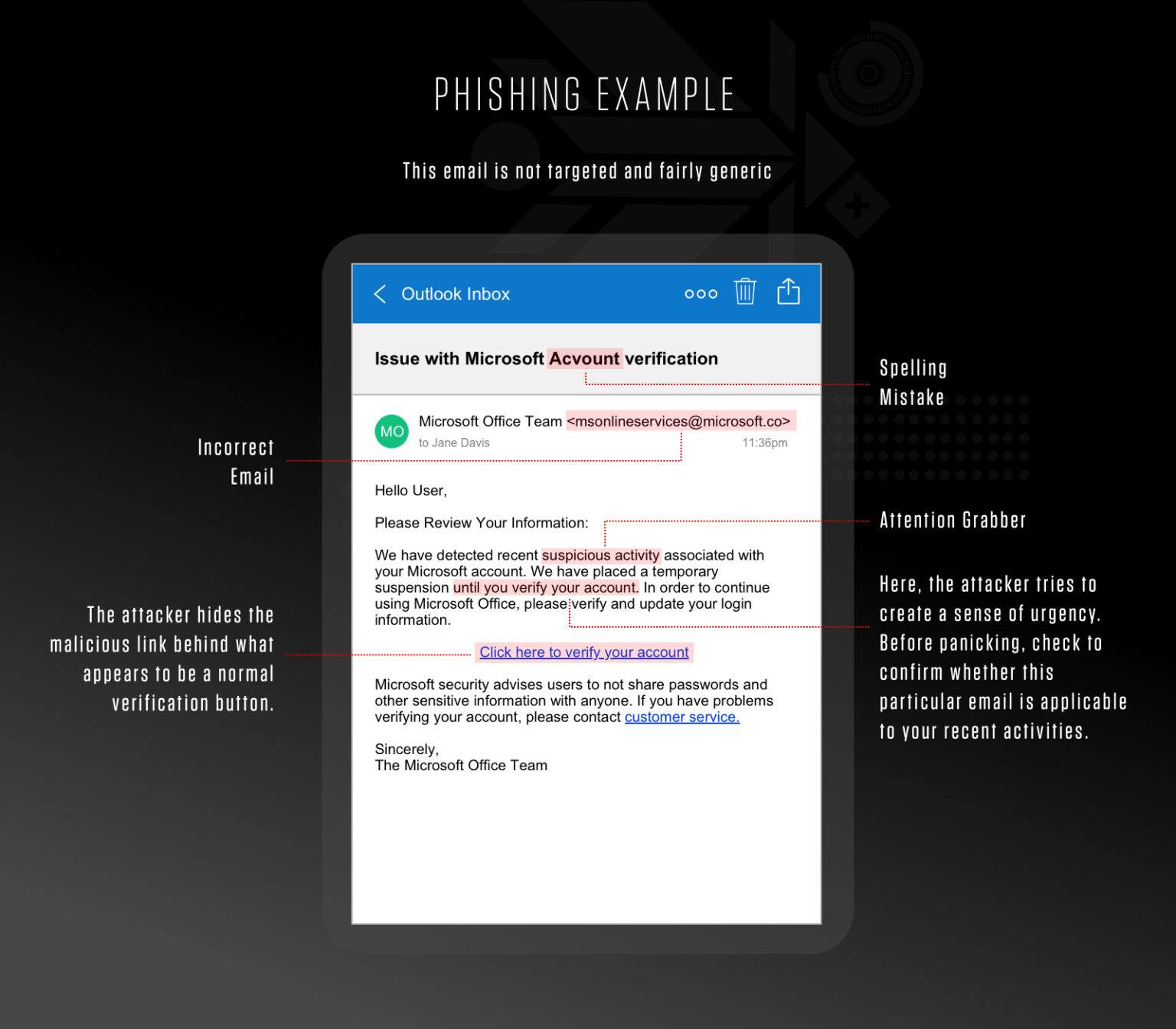
Why It Matters
- Massive growth — phishing attacks increased by 17.3% in early 2025 compared to late 2024 [APWG Report].
- AI‑powered deception — 82% of phishing emails now use AI to bypass filters and mimic human tone [KnowBe4].
- Human factor — 68% of breaches still involve human error, with phishing as the leading cause [Hoxhunt].
Common Phishing Techniques
-
Email phishing — fake emails that look like they come from trusted brands.

Fake PayPal email asking users to “verify” their account. -
Spear phishing — highly targeted attacks aimed at executives or employees.
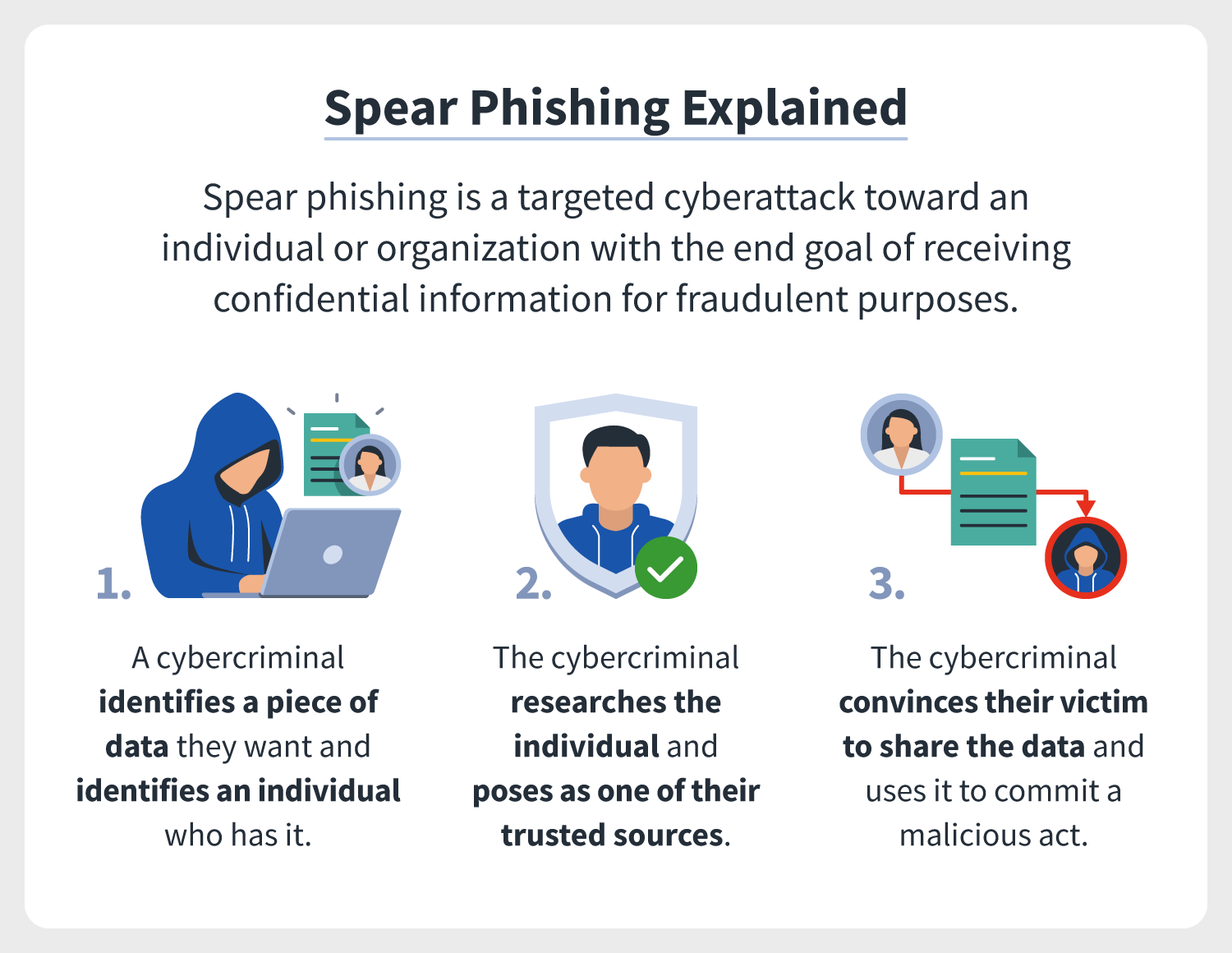
Spear phishing targets specific individuals with personalized details. -
Smishing — phishing via SMS or messaging apps.

Example of a fraudulent SMS pretending to be from a bank. -
Vishing — voice phishing, where attackers impersonate officials or IT staff.

Voice phishing (vishing) often involves fake calls from “support teams.” -
QR code phishing — malicious QR codes redirecting users to fake login pages.
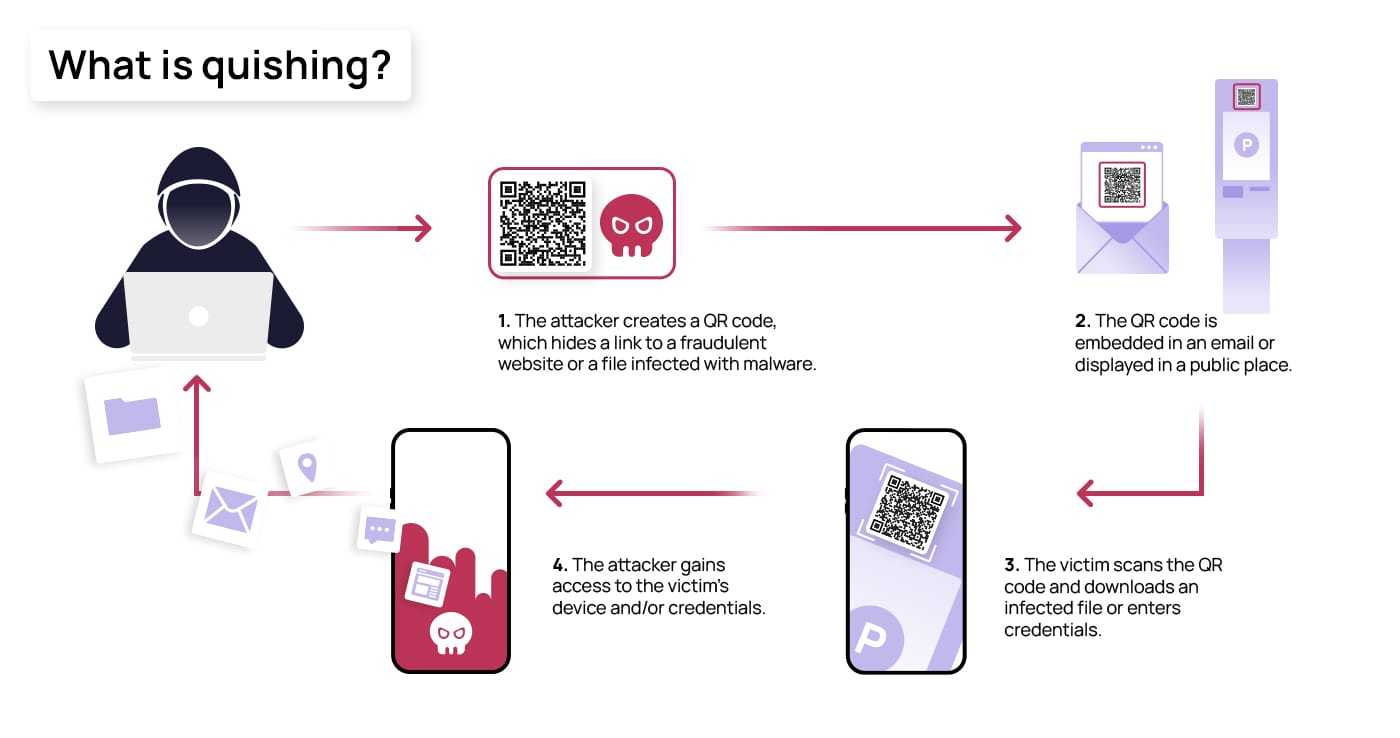
QR code phishing (“quishing”) tricks users into scanning malicious codes.
Risks Ahead
Phishing is no longer just about stolen passwords. In 2025, attackers use it to deliver ransomware, steal cryptocurrency wallets, and infiltrate supply chains. With AI generating endless variations of phishing lures, traditional spam filters are struggling to keep up.
How to Protect Yourself
- Verify links — hover before you click, and check for HTTPS and correct domains.
- Enable MFA — multi‑factor authentication stops most account takeovers.
- Security awareness — train yourself and your team to spot suspicious emails and messages.
- Use password managers — they auto‑fill only on legitimate sites, blocking many phishing attempts.
- Report attacks — forward suspicious emails to your IT/security team or report to anti‑phishing groups.
Conclusion
Phishing is evolving faster than ever, but awareness and layered defenses can keep you safe. By staying alert, verifying communications, and using modern security tools, you can avoid becoming the next victim of this AI‑driven cyber threat.
Hashtags
#Phishing #CyberSecurity #AIThreats #InfoSec #ZiBiSec #Awareness

